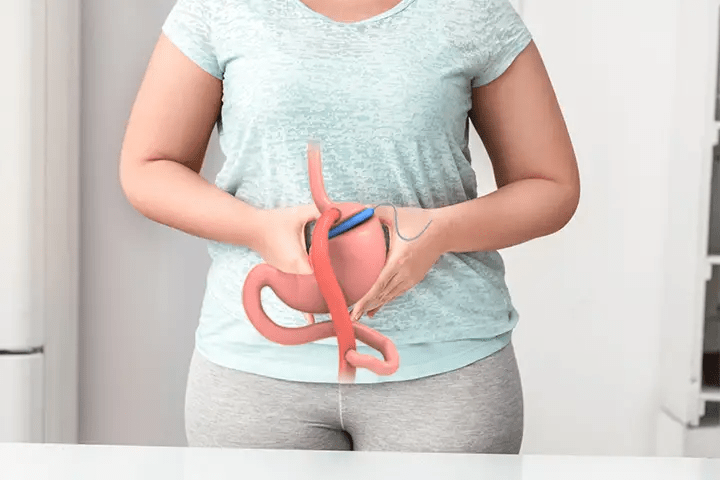
Gastric bypass is one of the most effective and recurrent bariatric surgery techniques when treating patients with severe and morbid obesity. The main characteristic is that the stomach of the person who undergoes this surgical intervention is considerably reduced and connects with the first section of the small intestine. This last step causes what is known as food malabsorption, a trait to which the main drawbacks of this method are associated.
The gastric bypass is the most common operation in the bariatric surgery , due in part to having a high degree of long term effectiveness as it is one technique in which more experience is within the field (over 34 years ).
Gastric bypass risks
Of course, as in other weight loss surgeries or higher-grade interventions, the technique presents potential health risks.
There is the potential for excessive bleeding, infections, adverse reactions to anesthesia, blood clots, respiratory problems, gastrointestinal leakage, and even death.
That is why it is very important to put yourself in the hands of the best specialists and surgeons who are experts in performing these types of interventions. And although the risks must always be kept in mind, it should be remembered that it is one of the techniques with the lowest rate of surgical risk (1.3%).
What are the drawbacks of gastric bypass?
Basically these are related to the malabsorption of food that causes the connection of the stomach to the first section of the small intestine. With this, less fat and carbohydrates enter the bloodstream, something positive when it comes to losing weight. However, the intestine also prevents some basic proteins and vitamins from being adequately absorbed, something that can lead to nutritional deficiencies in the patient.
“The lack of some of these nutrients in the diet can cause weaknesses in the hair or teeth, which can be solved with the appropriate intake of vitamins and supplements,” says Dr. Héctor Bernal , surgeon specializing in metabolic surgery and obesity.
Healthy diet and healthy lifestyle after gastric bypass
The partial and controlled malabsorption of nutrients –especially of sugars and fats- that occurs with this bariatric technique can be very effective, but it is also important that the patient undergoes exhaustive nutritional monitoring after undergoing gastric bypass.
“It is essential that the gastric bypass patient has postoperative nutritional monitoring by a Dietitian-Nutritionist , who trains him in healthy eating habits and helps him to make his own diet, understood as a healthy diet”, says Lydia Amador Martí, graduated in Nutrition and Dietetics.
The patient’s diet after the intervention must:
- Be divided into various intakes, the 3 main (breakfast, lunch, dinner) and the 2 secondary (lunch, snack). Increase intakes if the patient performs intense physical activity between meals.
- Be a very varied diet, full of nutrients and supplemented with vitamins and minerals. It should also include a high percentage of hydrating fluids.
- Be a diet low in sugar and fat. Although our body absorbs less, that does not give us a wide sleeve to eat wrongly; This will only make us regain the lost weight or even not lose anything.
- Be accompanied by healthy lifestyle habits. It is important to do frequent physical activity and avoid sedentary lifestyle to achieve maximum effectiveness.


GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings